Ethernet switches play a crucial role in networking infrastructure, facilitating seamless communication and data transfer within organizations. There are many brands of PoE switches on the market, and the FS S3410-48TS-P switch has become one of the many choices due to its performance. The Aruba 2530 series also performs well in terms of performance. What’s the difference between the two? How to choose? This article gives you the answer.
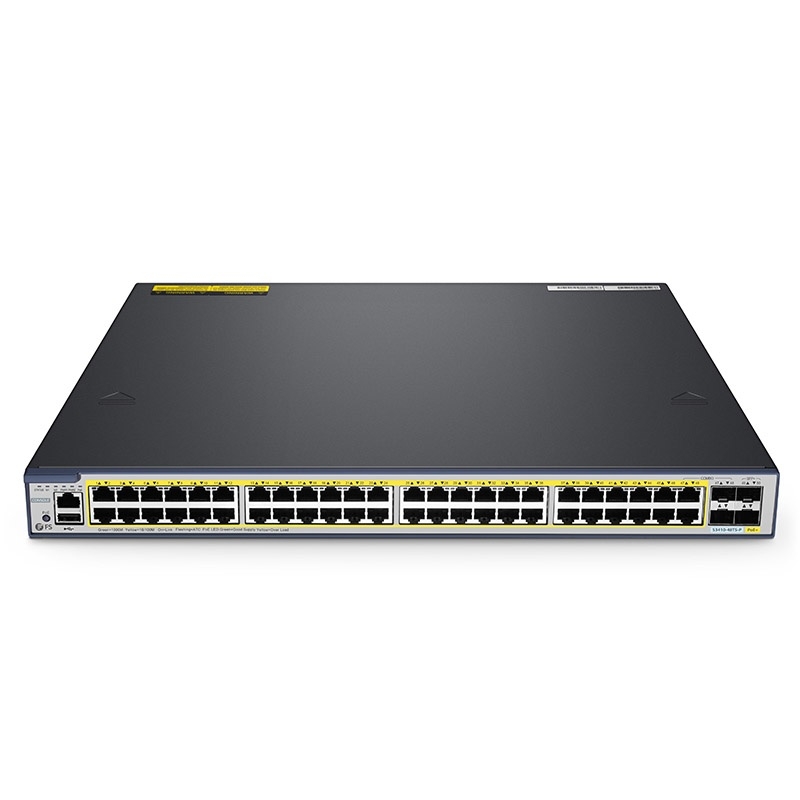
Overview of FS S3410-48TS-P
The FS S3410-48TS-P is a 48-port PoE managed Ethernet switch designed to meet the demands of modern network environments. Its key features include Power over Ethernet (PoE) support, gigabit Ethernet ports, and advanced management capabilities. The switch is well-suited for applications such as IP surveillance, VoIP, Wi-Fi access points, and other scenarios requiring both data and power delivery over a single network cable.
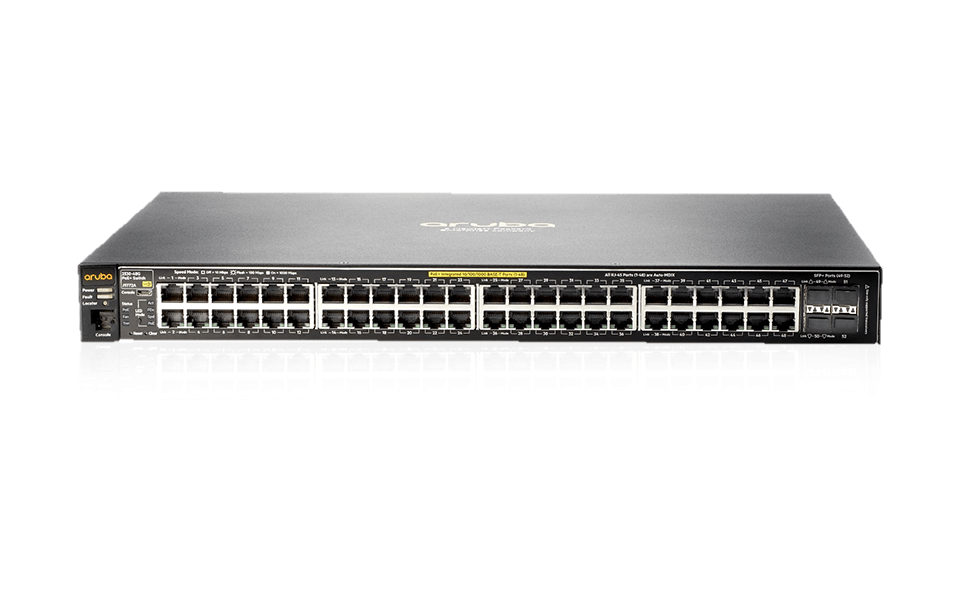
Overview of Aruba 2530
The Aruba 2530 (J9772A) is another prominent player in the Ethernet switch market. It offers a range of models with varying port configurations to cater to different network requirements. The switch is known for its reliability, security features, and ease of management. It is often deployed in enterprise networks, providing connectivity for devices across various departments.
The differences between FS S3410-48TS-P and Aruba 2530
Port Configuration and PoE Support
FS S3410-48TS-P: As the name suggests, this switch boasts 48 gigabit Ethernet ports. Moreover, it supports Power over Ethernet (PoE), allowing the delivery of power to connected devices like IP cameras and phones.
Aruba 2530: The Aruba 2530 also comes in various port configurations. Depending on the model, it offers a mix of Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet ports. PoE support is available in selected models, providing flexibility for organizations with diverse connectivity requirements.
Throughput and Bandwidth
FS S3410-48TS-P: With its gigabit Ethernet ports, the FS S3410-48TS-P delivers high throughput and ample bandwidth to handle data-intensive applications. It is suitable for environments where large data transfers and low latency are critical.
Aruba 2530: The Aruba 2530 offers competitive throughput and bandwidth, ensuring efficient data flow within the network. Its gigabit Ethernet ports contribute to low-latency communication, making it suitable for enterprises with demanding networking needs.
Management Capabilities
FS S3410-48TS-P: This switch provides robust management capabilities, including support for SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) and a user-friendly web interface. Network administrators can easily monitor and configure the switch to optimize performance.
Aruba 2530: The management capabilities of Aruba switches are relatively powerful. The Aruba 2530 features web-based management, SNMP, and other tools that simplify network administration tasks. It also supports role-based access control for enhanced security.
Security Features
FS S3410-48TS-P: Security is a paramount concern in modern networks. The FS S3410-48TS-P incorporates features such as Access Control Lists (ACLs), port security, and DHCP snooping to enhance network security and mitigate potential threats.
Aruba 2530: Aruba switches are equipped with security features like IEEE 802.1X network access control and port security. These features contribute to the overall network security posture, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data integrity.
How to Choose FS S3410-48TS-P and Aruba 2530?
The FS S3410-48TS-P excels in environments where PoE support for a large number of devices is crucial. Its gigabit Ethernet ports and robust management capabilities make it a suitable choice for applications demanding high throughput and efficient network management. On the other hand, the Aruba 2530 stands out for its reliability, security features, and ease of management. It is well-suited for enterprise networks where a balance between performance and security is essential.
Ultimately, organizations should carefully evaluate their networking needs, consider scalability, and assess the long-term value each switch brings to the table. Whether prioritizing PoE support, high throughput, or advanced security features, making an informed decision ensures that the chosen Ethernet switch aligns seamlessly with the organization’s current and future networking requirements.
Related Articles:
PoE vs PoE+ vs PoE++ Switch: How to Choose?
PoE Switch vs PoE Injector: Why Choose PoE Switch to Build Wireless Networks?