Transceiver module temperature has an important effect on the function of communication system. If the temperature of transceiver module is over its given range, it will cause transmission delays, drastically reduced output and network partitions. This article will give a clear explanation for the transceiver module temperature.

Figure 1: Transceiver modules
What Is Transceiver Module Temperature?
The transceiver module temperature determines the available temperature of transceiver modules. According to different types and brands, transceiver modules may have different temperature ranges. For example, the temperature range of optical transceiver is larger than copper module, and the temperature range of SFP module is smaller than SFP+ module such as 1000BASE-SX SFP is from 0 to 70°C while 10Gbase-SR is from -40°C to 85°C. Conventionally, the transceiver module temperature mainly includes three levels: commercial temperature range (COM: 0~70°C), extended temperature range (EXT: -20°C~85°C), and industrial temperature range (IND: -40°C~85°C).
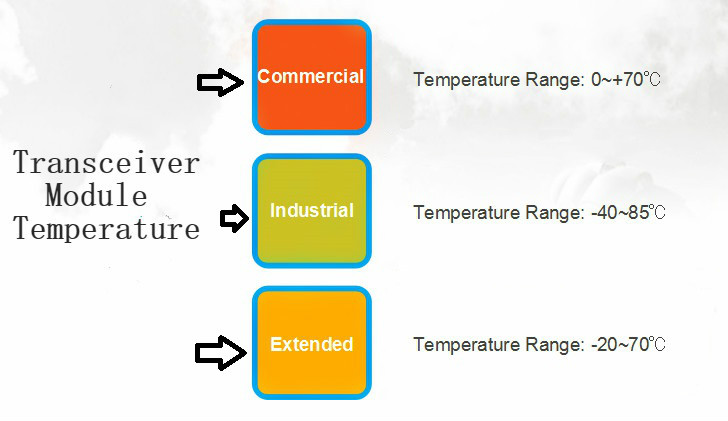
Figure 2:Transceiver module temperature
Why Suitable Temperature Is Needed on Transceiver Module?
Each transceiver module has its operating temperature range. If the temperature is too high or too low, the transceiver module will not work normally.
If the operating temperature is too high, its optical power will become larger and the receiving signal will be incorrect, which leads to the disordered operation of the transceiver module. Or even worse, the transceiver module would be burned. Facing this problem, you can add a temperature control system for real-time monitoring and compensation. It can ensure the transceiver module extinction ratio and stable luminous power, which helps the optical system work normally.
If the operating temperature is too low, the function of the transceiver module also will be unstable. Usually, the temperature of the transceiver module will not be too low as long as the transceiver is not put in the environment with a temperature below 0°C.
What Can Affect the Transceiver Module Temperature?
When a transceiver module is being used, the power consumption and case surface will affect its temperature. Except these, there are mainly three aspects that affect the transceiver module temperature.
- Poor quality – The transceiver module with poor quality has unstable function and poor heat dissipation. As a result, the abnormal temperature of the transceiver module will happen very frequently. While, if you use the transceiver module with better quality and workmanship, the temperature anomaly and unnecessary discard will be reduced.
- Harsh application environment – Transceiver modules are commonly used in the computer room, home networks, and data center. If they are applied in other harsh environments such as oil, deserts, mountains and so on, the temperature of these transceiver modules will be changed by the ambient environment. Then their optical power and optical sensitivity will be damaged.
- Using second-hand transceiver modules – As mentioned above, the temperature of a new transceiver module is at 0-70°C. While the temperature range of the second-hand transceiver module is smaller than the new one. Because some functions of the second-hand one have degenerated.
Conclusion
Transceiver module temperature stability is an important factor to ensure module work normally. FS.COM provides comprehensive transceiver modules which have a wide temperature range with a very high tolerance level, such as the compatible GLC-LH-SMD module covering commercial temperature from 0 to 70°C. All modules from FS are 100% tested and have a reliable quality. If you have any needs, welcome to visit FS.COM.
Related Article: SFP Module: What’s It and How to Choose It?