Background
In order to satisfy peple’s higher and higher demands of the network speed, technology been developed rapidly. In just a few decades, the network speed has a leap from 10Mbit/s in 1983 to todays 40/100 Gbit/s. We can see the figure 1, it clearly shows the development of network speed and technologies during 1983 to nowadays. Assuming a few decades ago, we couldn’t possibly imagine that we would now use such high speed network in our lifes. It is really amazing! With the advance of science and technology, I believe we will certainly surpass the 40/100 Gbit/s technology one day.
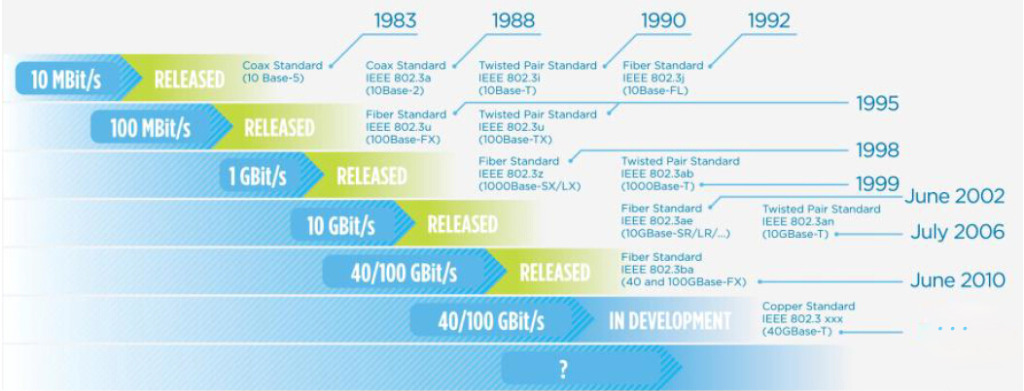
Figure 1. Development of Network Speed and Technology
10/40/100 Gbit/s – the transition is occurring right now
What are people saying about their 10/40/100 Gigabit Ethernet Migration Plans? You can easily understand through the following diagram (Figure 2). Fiber optic cables become more and more widely used than the copper cabling. About fiber, the OM3/OM4 multimode fibers have been more and more important with the development of the network speed. However, it do not mean that fiber will entirely replace the copper cabling because the copper- and fiber-based equipment interconnect options will continue over time (Figure 3).
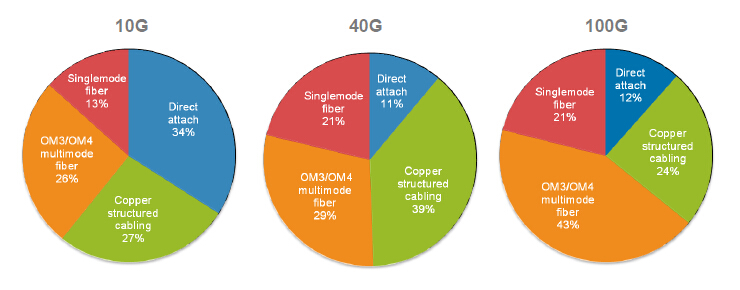
Figure 2. 10/40/100 Gigabit Ethernet Migration Plans
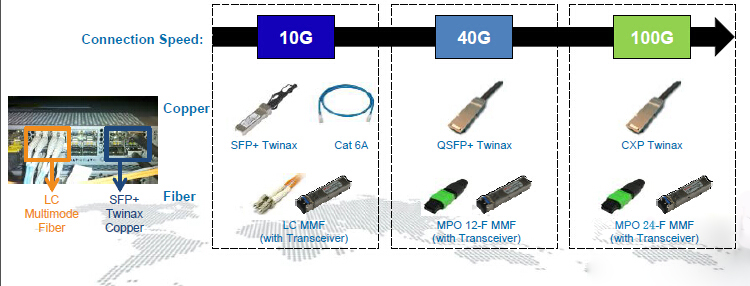
Figure 3. Nowadays Equipment Interconnect Options
You may wonder that how do they connect and what devices will be need to support the high speed except the cables.
Types Of Interfaces For Ethernet
In general, there are three types of interfaces for Ethernet as the following (Figure 4):

Figure 4. Types of Ethernet Interfaces
- Copper – RJ45
- Fiber – Build-in modules LC/SC/MPO
- Pluggable Transceivers Modules
Pluggable Modules Introduction
As the Figure 5 shows, according to the interface of Ethernet, the common used pluggable modules include the three types. Copper cable, usually with RJ45, direct attech cable and the pluggable transceiver modules with the patch cables.
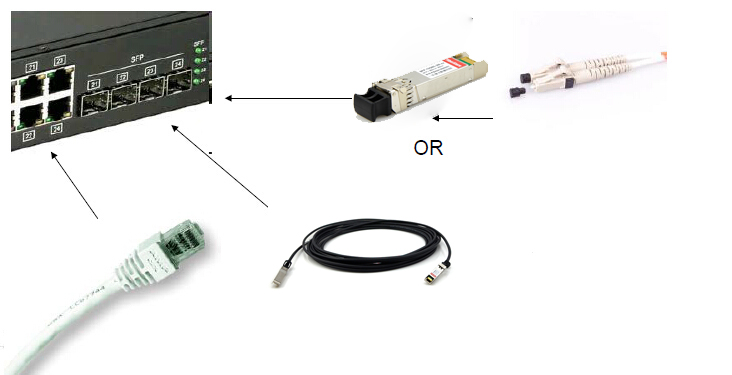
Figure 5. Pluggable Modules
Accoring to the difference function or application, even the standard of the pluggable transceivers, there are many kinds of them. The commonly available pluggables include the SFP, SFP+, XENPAK, X2 etc. In addition, with the development of the technology and the higher demands of the network speed, QSFP/QSFP+ , XFP and the CFP are now gradually used in many fields. (For example as Figure 6)
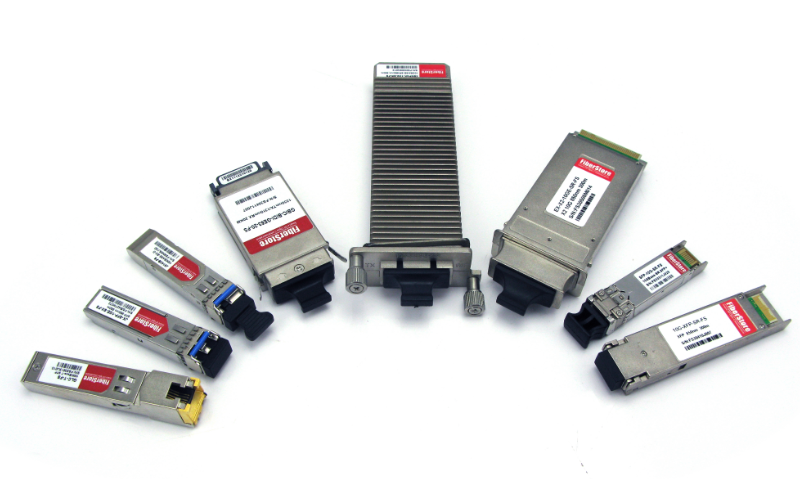

Figure 6. Some of The Commonly Available Pluggables
- SFP – Support 1.25Gbit/s to 4.25 Gbit/s.
- SFP+ – An enhanced version of the SFP that supports data rates up to 10 Gbit/s.
- QSFP/QSFP+ – Up to 10 Gb/s per channel, total 40G interface.
- XFP – XFP is a standardized form factor for serial 10 Gb/s fiber optic transceivers.
- CXP – Adopted for 120G InfiniBand and 100G Ethernet.
- Direct Attach Cable – Copper or Fiber.
Standards Drive the Market for High Speed Interfaces
In order to control the market of a variety of products that used to support high speed network, many standards are published to make standardization: (Figure 7)

Figure 7. Related Standards
More knowledge the Pluggable Modules can visit here!
Product needs, welcome to Fiberstore!