Though the Cat8 patch cable is arousing more and more attention in the market, the previous generations of patch cables such as Cat6 still play an important role in wired networks. At present, Cat6 cable can be categorized by shielding type, conductor type, flame retardant class, costs, length, color, etc. And it is widely used in home, SMB applications, and data center where up to 10GBase-T networks are used. Cat6 cable can meet the requirements of fast transmission and excellent signal quality. Then how to choose suitable Cat6 cables for different applications? This article may show you some clues.
Overview of Cat6 Cables
Defined by EIA/TIA standards, Cat6 (Category 6) patch cable is the sixth generation of twisted pair Ethernet cabling. It contains four pairs of copper wires and uses all the pairs for signaling in order to obtain its high level of performance. Being backward compatible with all the previous categories, Cat6 cable operates at up to 250 MHz. And it can support up to 1000BASE-T within 100m and 10 Gigabit Ethernet over the limited distance (37-55 meters) specified in the industry. Due to its high data transfer speeds and dependability, Cat6 cable is widely used in home, business networks, and data centers.

Figure1: Cat6 patch cable
What Need to Consider When Choosing Cat6 Cables?
The appropriate application of Cat6 cables can help save money, decrease the install and maintenance time, and meet the future-proofing network requirements. So it is necessary to know how to choose suitable Cat6 cables. Actually, to buy suitable Cat6 patch cable, many factors can be taken into consideration, such as shielding type, conductor type, flame retardant class, etc. Here, we have summarized several main features that help you choose suitable cables for different scenarios.
The shielded cable is a twisted pair cable confined in foil or mesh shield that helps protect the data from high electromagnetic interference(EMI) or radio-frequency interference (RFI). The EMI/RFI is produced when cables are close to power cables, RF devices or some high-power machines. This will slower transmission speeds and create more data errors. Therefore, shielded Cat6 cable has faster transmission speed and fewer data errors, which is ideal for high-speed networks such as data centers.
Due to the twisting of the wire pairs, unshielded Cat6 cable helps reduce noise and crosstalk, and can offer some resistance to EMI/RFI but less effective than the shielded cable. The unshielded Cat6 cable is less expensive than shielded cable, and easier to install since no shielding and the drain wire involved. It is the most common type used in desktop communications applications.
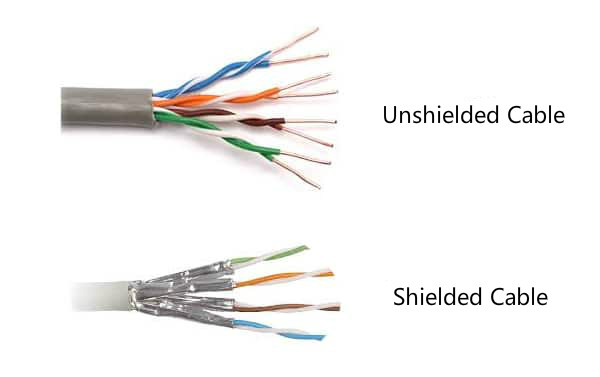
Figure 2: Shielded cable and unshielded cable
Solid cable uses a single piece of copper for the electrical conductor that is designed for backbone and horizontal cable runs. Due to the large core, solid cable is durable but not so flexible that it shouldn’t be bent or twisted repeatedly. And with the better attenuation, solid cable is able to support longer distance transmission and higher data rates.
Stranded cable uses a series of copper cables twisted together. It is more flexible than solid cable, but has high attenuation. So the stranded cable is used for short distance transmission between wall plates and interface cards, hubs, and other rack-mounted equipment. Moreover, compared to solid cable, stranded cable has more expensive production costs.
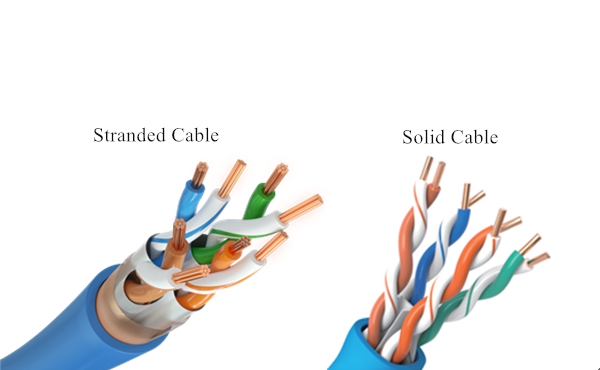
Figure 3: Solid cable and stranded cable
Riser cable or CMR cable is referred to as “riser-rated cable” and designed to prevent fires from spreading between floors through risers or vertical shafts. Therefore, the riser cable is appropriate for in-wall installation of Ethernet cables, and the installation inside a residence or a single-story commercial building.
Plenum cable or CMP cable is referred to as “plenum-rated cable”. Its jacket is made from material that retards the spread of flames, and does not give off much smoke or toxic gas when burned. Hence, plenum cable is suitable for installation into air plenum spaces such as drop ceilings and raised floors.
The cable length and color also need to be considered when choosing Cat6 cables for your network. Cat6 patch cables can come in short lengths such as 0.15m, or longer lengths such as 61m. Moreover, custom lengths are available. The cable length you need mainly depends on two aspects. One is the distance between your network devices, and the other is the extra length for future capacity expansion. In terms of the color, various colors are available such as red, blue, gray, white, etc. Among them, blue may be the most common one. Different colors can distinguish different applications, but the ultimate decision is based on your preference.
Summary
Cat6 patch cable, as an advanced Ethernet cable, is widely applied in cabling system now. Choosing the right Cat6 cable matters a lot to your network deployment. So all factors mentioned above, including shielding type, conductor type, flame retardant class, length, and color need to be weighed up. FS provides a variety of high-quality and cost-effective patch cables, which have 100% passed the Fluke Test. If you have any needs, welcome to visit FS.COM.
Related Articles:
Quick View of Ethernet Cables Cat5, Cat5e And Cat6
How to Choose the Right Cat6a Cable for Your 10G Networks