DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a combination of a set of optical wavelengths that can be transmitted with one fiber. This is a laser technology used to increase bandwidth on existing fiber-optic backbones. It enables optical fiber networks to transmit signals of several wavelengths simultaneously. In DWDM system, Mux/Demux are two indispensable components. How do these two components work in DWDM system and how to choose a DWDM Mux/Demux? We have the answers for you in the following contents.
What Is DWDM Mux/Demux
To understand DWDM Mux/Demux, you have to know what DWDM is. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is an optical multiplexing technology used to increase bandwidth over existing fiber optic backbones. The data from various different sources is put together on optical fiber in which each signal travels at the same speed on its own light wavelength. In DWDM system, Mux/Demux are two indispensable modules. Mux (Multiplexer) is a module at the transmitter end that brings several data signals together for transporting over a single fiber, while Demux (Demultiplexer) is a module at the receiver end that separates the signals that come together and passes each channel to an optical receiver. DWDM Mux/Demux modules are made to multiplex multiple DWDM channels into one or two fibers. It can extend the bandwidth of optical communication network with low cost and long transmission distance, which makes it an ideal network solution.

How Does DWDM Mux/Demux Work
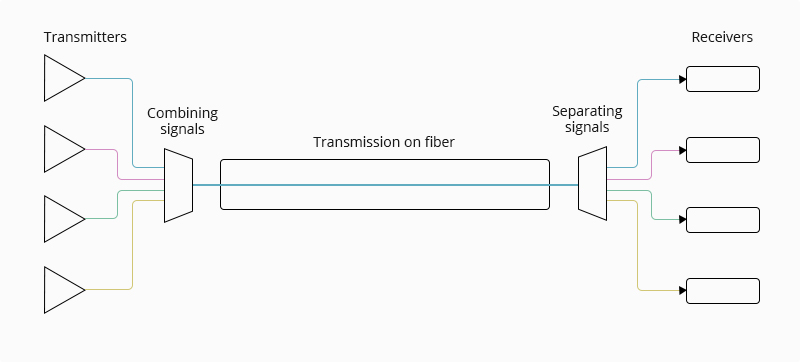
The DWDM network structure begins with transponders or transceivers accepting data input from a variety of traffic types and protocols. This forwarder performs the basic function of mapping input data to a separate DWDM wavelength. Each individual wavelength will be fed to the Mux, and the Mux filters and combines multiple wavelengths onto a single output port for transmission through the main DWDM fiber. Then, at the receiving end, individual channels can be isolated by using Demux to separate wavelengths, and each channel can then be routed to the appropriate client-side output via additional wavelength-matched transponders or transceivers. The picture below can be a good reference.
Factors to Consider When Choosing the DWDM Mux/Demux
Line Port
Line port is one of the important ports for each DWDM channel multiplexing and demultiplexing. There are dual fiber and single fiber types of line port, and which to select depends on the use of DWDM wavelengths. As for single-fiber DWDM Mux/Demux, it requires only one single optical fiber to transmit the signals. However, the transmission line can be either unidirectional or bi-directional. Single-fiber unidirectional indicates that optical modules are connected through only one optical fiber and signals can only be sent from the transmitter to the receiver, not in reverse. The advantage of this transmission is that the system is relatively easier to design and more convenient for separate wavelength monitoring. Picture below can be the reference for single-fiber unidirectional transmission.

Single-fiber bi-directional is used to transmit and receive optical signals in two directions at the same time in an optical fiber, just like the positive and negative lanes separated by the separation belt on the road. Vehicles on both sides of the road run in their own lanes without interfering with each other. The advantages are also obvious. Single fiber bidirectional technology can use only one fiber to complete the work that two fibers can do, the existing fiber transmission capacity has been doubled, thus greatly saving fiber resources. Picture below can be the reference for single-fiber bi-directional transmission.

Dual-fiber DWDM Mux/Demux uses two optical fibers, one of which only transmits the optical signal in one direction, while the other transmits the optical signal in the other direction. The advantage is that dual-fiber DWDM Mux/Demux requires two fibers for transmission, each signal is carried by different wavelengths and will not affect each other, the reliability would be higher.

Channel Port
Like line port, channel port is another important port. A DWDM Mux/Demux usually has several channel ports on different wavelengths and each channel port works for a specific wavelength. The channel port of a DWDM Mux Demux is usually ranging from 4 to 96, using the wavelength ranging from 1470nm to 1625nm with a channel spacing of 0.8nm (100GHz) or 0.4nm (50GHz). A DWDM Mux/Demux with more channels offers more capacity, yet the price would be higher as well.
Monitoring Port
Except for the must-have line port and channel port, DWDM Mux/Demux can also be added with other ports such as monitoring port for better network monitoring and management. The monitoring port offers flexible monitoring ways to test the power, wavelength and optical-signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) of the optical signal without service interruption. Besides, early warning can be provided in time if there is any deviation. Therefore, it can also improve the stability of system transmission. The monitoring port can be either a simplex or duplex fiber port, which depends on the type of DWDM Mux/Demux you are using. The simplex fiber port can monitor only the DWDM, while the duplex fiber port can monitor the entire network.

Active/Passive DWDM Mux/Demux
DWDM Mux/Demux can be divided into active DWDM Mux/Demux and passive DWDM Mux/Demux according to whether the device needs power supply or not. Active DWDM Mux/Demux indicates the device needs power supply.
An active DWDM Mux/Demux includes wavelength adjustable laser, wavelength adjustable filter and wavelength selective amplifier, etc. Active setups grant you more control over your optical network, you can dynamically re-tune wavelengths without dropping connections. Active DWDM Mux/Demuxs are widely used in large capacity optical transmission applications.
“Passive” indicates the DWDM Mux/Demux is an unpowered, pure optical equipment. It requires zero maintenance, upgrades, or electricity to function properly. A passive DWDM Mux/Demux includes dispersion device, interference device, optical coupler and so on. Passive DWDM Mux/Demux is a plug and play system, which is simple and convenient to use. It is mainly applied to the access layer of MAN, campus network, enterprise network and various special industry networks (such as banking, public security, etc.). At present, passive DWDM Mux/Demux is widely used in optical fiber communication solutions.
However, passive DWDM Mux/Demux does not have the OAM function, and does not have protection means in case of link failure. To solve this problem, another type of DWDM Mux/Demux has been developed by FS. Based on the passive DWDM Mux/Demux, it adds optical switches, optical splitters and other devices in optical fiber link. This DWDM Mux/Demux device needs to be connected to the power supply by default, when the power is on, it can be used as an active DWDM Mux/Demux to monitor each port in real time; when the power is off, the device can still be used as a passive DWDM Mux/Demux without affecting the link transmission. It combines the advantages of active and passive DWDM Mux/Demuxs, and effectively solves the shortcoming of passive DWDM Mux/Demux which cannot be managed and maintained through the intervention of active equipment. Therefore, it is now becoming a more popular deployment choice in networking solutions.
Packaging Types
DWDM Mux/Demux come in three different packaging forms – 1U 19″ rack-mounted, FMU plug-in and splice/pigtailed ABS box. The first type is in 19″ rack-mounted package, easy for installation. The second one can be used with 19″ rack chassis, which is very convenient for use by just plugging in. The last one is in ABS box package based on standard thin film filter (TFF) technology and its pigtails are labeled with wavelengths. It takes little space and can be installed in various chassis. Pictures below can show more details.

Summary
To improve the efficiency of network transmission, DWDM technology is often deployed in the devices. DWDM Mux/Demux is now recommended as one of the most cost-effective network solutions with expanded fiber capabilities. Hope the above explanation on its working principles and the analysis of different factors can help you make the best choice on the DWDM Mux/Demux for your network.
Article Source:DWDM Mux/Demux Overview-Working Principle and Different Types | FS Community
Related Articles:
An Overview of DWDM Technology and DWDM System Components | FS Community