Big Data, Internet, video and cloud computing are driving relentless bandwidth growth and increasing demands on service provider, enterprise, and government networks. The appearance of a new technology which is high-performance applications, scale more easily, operate more efficiently and reduce costs seems to be the trend of the times. So, now what? Most are turning to Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology in order to increase capacity around the fiber links which are already in place!
What Is Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology?
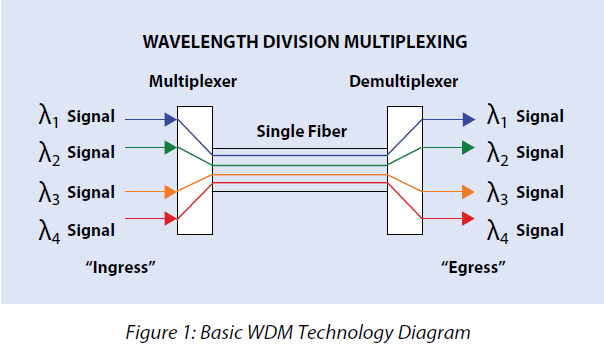
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is really a technology which multiplexes multiple optical signals on one fiber by utilizing different wavelengths, or colors, of laser light to carry the various signals. Through the use of bidirectional communications on the single fiber, network managers can realize a multiplication effect within their available fiber`s capacity. There is a simple example concerning the WDM technology. If each color of light carries a data rate of 10 Gbit/s, then, combining 4 colors of light in to the same fiber increases the total data rate fourfold to 40 Gbit/s.
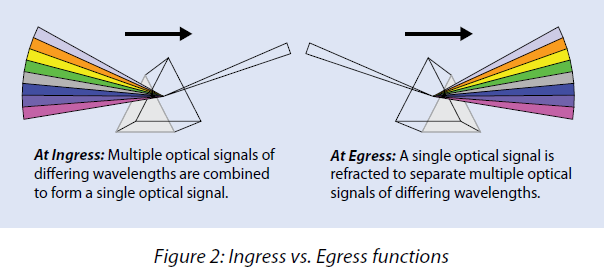
In addition, there are two critical factors inside a Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) system which is the optical wavelength multiplexer (MUX), and also the de-multiplexer (DEMUX). We are able to begin to see Figure 2 below, an optical prism represents a handy method to understand a MUX/DEMUX function. Whenever a multi-color light beam goes through an optical prism, because of its unique material property and geometry, the light of various colors will exit at different angles and become, in WDM terminology, optical de-multiplexing. Conversely, if the light of multi-colors is sent through the prism at different predesignated angles, they’ll exit the prism in the same angle like a single light beam becoming, in WDM terminology, optical multiplexing.
CWDM MUX/DEMUX (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer/Demultiplexer)
CWDM MUX/DEMUX is a flexible and low-cost solution that allows the development of existing fiber capacity. Along with highly reliable passive optics certified for environmentally hardened applications, the CWDM MUX/DEMUX solution lets operators take advantage of available fiber bandwidth in local loop and enterprise architectures.
Advantages of CWDM:
- Passive equipment that utilizes no electrical energy
- Much lower cost per channel than DWDM
- Scalability to develop the fiber capacity when needed
- with little or no increased cost
- Protocol transparent
- Simplicity of use
Fiberstore CWDM MUX/DEMUX Products
Fiberstore supplies a complete portfolio of CWDM MUX/DEMUX to match all applications, for example, Gigabit & 10G Ethernet, SDH/SONET, ATM, ESCON, Fibre Channel, FTTx, and CATV. And that we provide optional port configurations, for example, Express Port, Monitor Port,1310nm passband port and 1550nm port of these multiplexers based on customer choice.
DWDM MUX/DEMUX (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer/Demultiplexer)
DWDM MUX/DEMUX may be the technology preferred by transporting extremely large amounts of information traffic over metro or long distances in telecom networks. Optical networking and especially using DWDM technology has proven to be the optimal method of combining cost-efficient transport with advanced functionality, which could deal with the bandwidth explosion from the access network.
Advantages of DWDM:
- Up to 32 channels can be achieved passively
- Up to 160 channels by having an active solution
- Active solutions involve optical amplifiers to achieve longer distances
Fiberstore DWDM MUX/DEMUX Products
DWDM MUX/DEMUX modules are members of a number of high-end products according to silica-on-silicon planar technology. The AWG chips Fiberstore employed for DWDM MUX/DEMUX are focused on Long-Haul, Metro and access applications, where outstanding optical performance and occasional cost are paramount.
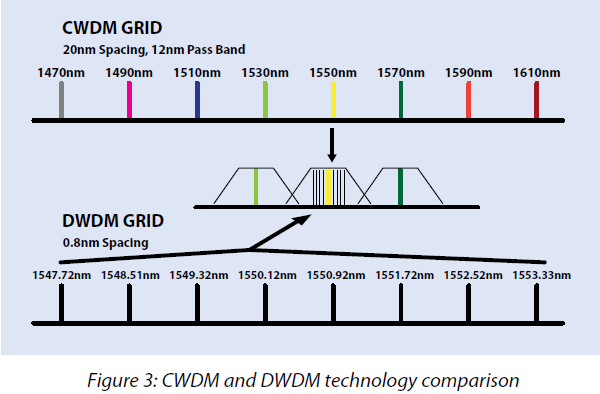
CWDM and DWDM technology Comparison
CWDM and DWDM both use the Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology, but with different features. As shown in the Figure 3, there is a comparison between CWDM and DWDM technology. A CWDM MUX/DEMUX deals with small amounts of wavelengths, typically eight, but with large spans between wavelengths(spaced typically at around 20nm). A DWDM MUX/DEMUX deals with narrower wavelength spans (no more than 0.8nm,0.4nm or perhaps 0.2nm), and may accommodate 40,80, or even 160 wavelengths.
Related Articles
CWDM vs DWDM: What’s the Difference?
How to Install Your CWDM MUX DEMUX System?